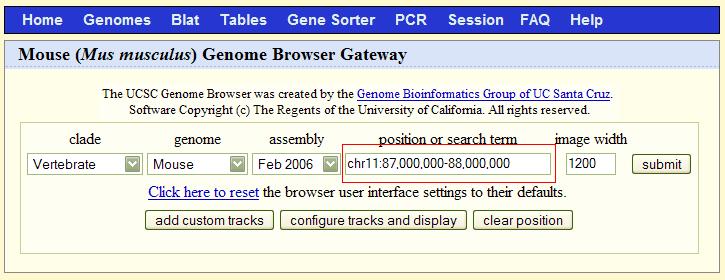
| Here is a gene view of TrpM8. The red circle indicates the known gene sequence, displayed as a piece of genomic DNA with both exons and introns. Clicking on the Trpm8 inside the red circle brings up additional gene information, including the DNA bases. | 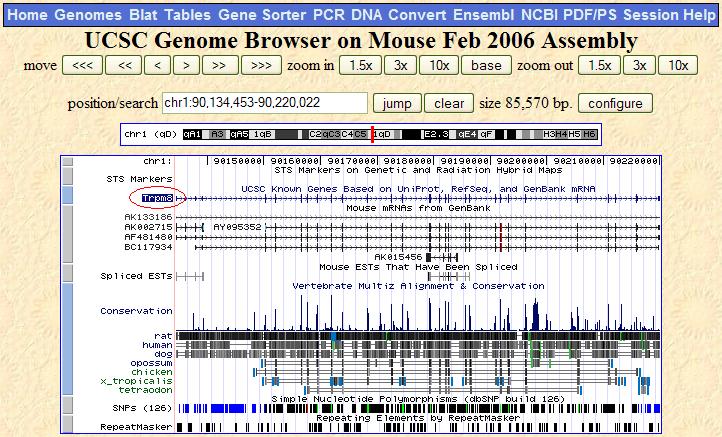
|
| Below the gene viewer are several parameters you can set. In this image, I am setting the map to display TrpM8 ESTs found in organisms other than mouse. Once the new parameters have been set, just hit the refresh button at the bottom of the gene viewer page to see the new results. | 
|
NCBI BLAST Database
| The NCBI BLAST Database contains many tools for searching and comparing gene and protein sequences. For the purposes of this quiz section, we are most concerned with the tools shown on the right. You can query for genes using DNA sequence (nucleotide blast), or query for proteins using amino acid sequence (protein blast), or query for proteins using DNA sequence (blastx). | 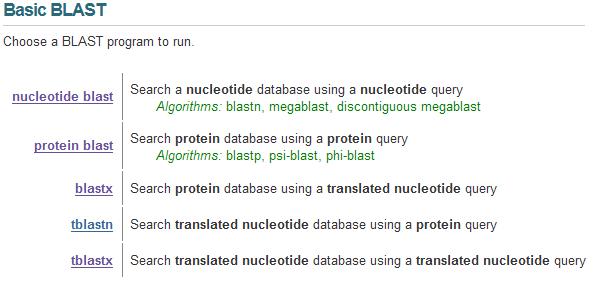
|
| The image on the right shows an example of using nucleotide blast. Sequence is entered in the box at the top. The database you want to search is chosen from the pull-down menu shown here. Once your parameters are set, just press the BLAST button in the lower left corner to begin your search. | 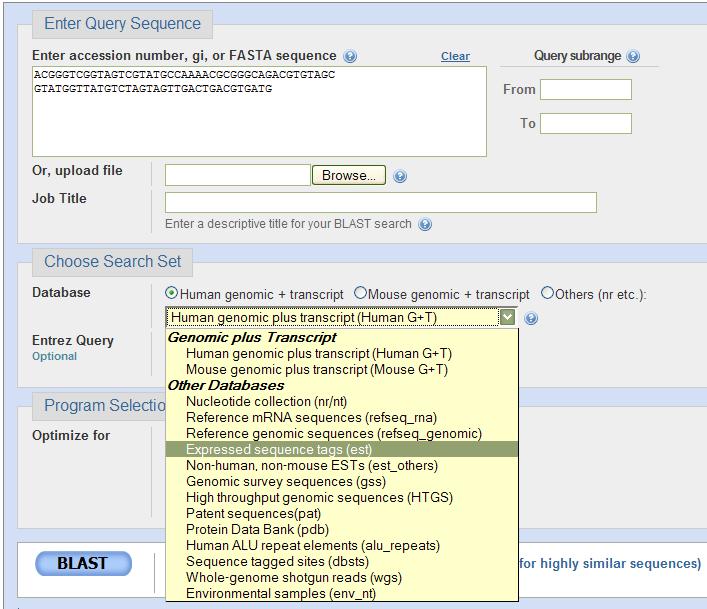
|
|
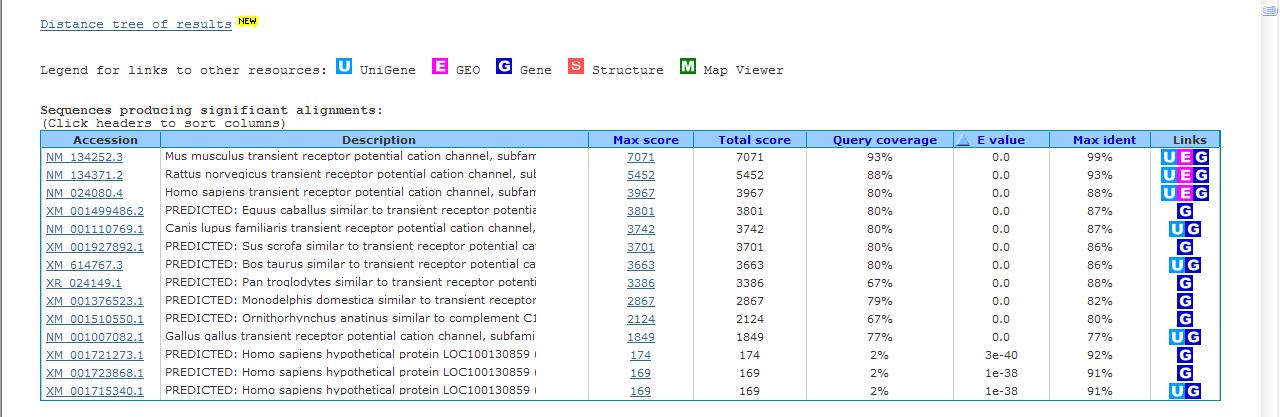
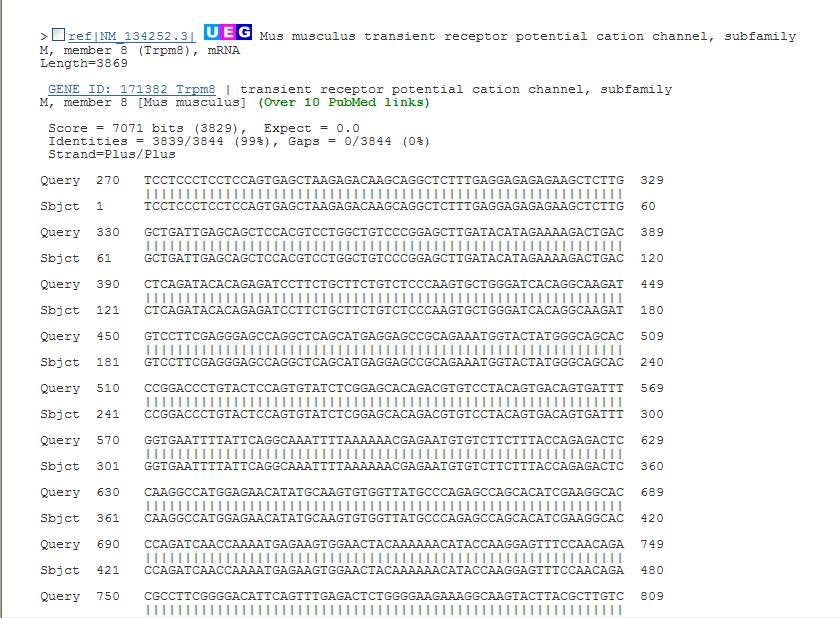
| Above is an example of a query using the mouse TrpM8 mRNA sequence and searched against the Reference mRNA sequence (refseq_RNA). Notice that there is highly conserved sequence found in other organisms. Each result has an Accession number that you can click on to obtain more information about the sequence from the database. When viewing the results, Query coverage indicates what fraction of the nucleotides align to the database sequence. E value indicates the probability of this match happening by chance, thus values are better the closer they are to 0. Max ident is the identity between the sequences. In other words a value of 100% means the query and database sequences match exactly, and a value of 90% indicates that 10% of the bases differ between the two sequences. Below shows one of the sequence alignments found in the list. You can use these to visualize the similarity between two sequences. |
|
Activity #1 [solution]
Step #1: Open the Mouse Genome Browser and find the following chromosomal segment: chromosome 11, bases 87 million to 88 million.
Step #2: Set the gene viewer image to only show known mouse genes.
Step #3: How many genes do you see?
Step #4: Pick a gene whose protein product is >500 amino acids. Using the NCBI BLAST Database, find its homolog in the dog, Canis familiaris. Is there a homolog in the dog?
Activity #2[solution]
The following sequence was obtained from mouse:
GTATCCAACGGTTGTGTGAGTAAAATTCTGGGCAGGTATTACGAGACTGGCTCCATCAGA CCCAGGGCAATCGGAGGGAGTAAGCCAAGAGTGGCGACTCCAGAAGTTGTAAGCAAAATA GCCCAGTATAAACGGGAGTGCCCTTCCATCTTTGCTTGGGAAATCCGAGACAGATTATTA TCCGAGGGGGTCTGTACCAACGATAACATACCCAGT
Step #1: Using any of the available tools, identify the gene.
Step #2: Find the accession number of the human homolog of the gene.
Step #3: What other organisms share homology to this gene? Name at least 3.
Step #4: What is the sequence identity of the gene between mouse and human?
Activity #3 [solution]
Here is a piece of unknown, non-human chromosomal sequence:
TTCCTACGAAGGAGAGCAGAAATCAATGCTCCTATTGCAGATAAATACATCCTAACATGT ATCTTAACTTTTACTGATTGTCCTAGTCACAGTGGATGCAGTGAAAAAATATTATGGATT TTTATGTGATGAGAATCTTGTCTTGTATTTACTATTTTGTCCCATTTTCCACATACTCTA TTTGACAAAGTGTGGTGTTAACAGGAGAATAAGATTTTACAGTGGTTAACATACCATTCA GATATCACAAAGACTTATAACAATGAAGTTGTGACTAATTCCCAGCAGGCATAACGATGC AGGGAAGAAAGGGAAAAAAAGGAAAAAAAAAATCACCTGTGTGTGAAGCCTACCTACACT ATTCTTCAGCCTTTTTAAAATTAGTATTTTTTTTCATCCCGTTCATGTGGGTGGAAGCAA GCTGCTACATTTAAGCCAGGATCCAGCAAAACAATTGGACATGTTCTTCAATGATGAAGA TCACAAATATTTGAGAGCATGTAACTGGGCTCTTCAGTCTGCTTATGGTGAGTTAAATGA GCCTCTTTTCGAAGGATCAGGAGCATGAGCTGTTTTACAAAAGCTCACTGCAAAACACTT CATGCCTTACGTGGTTTACTGAAATACTAGAGGCAGTTAAATCTCTGTGCTGAACTGTTA ACATACATTTTTTCAAGCTCATTATCTATGTGACTACAGGACTTGATTCAGCTCACTCAG AACTACAAAATGATCTCTCTGGTCCCCATTGACATTGCCAGAATTTCATGAGACGACCCA TGTCAACTCACTTAGGACAGAAGAAGAACCTTTGAACAGAACATGAGATGTTGCAAATAC TCAGGAAACCCAAACAGCAATCAAAGATCAAGTGTCCTTTTAAGTCTTTCACTGGATCAA GTTCTAGATGTCTAACACCTCTGGTTTTCAGCCTGACCTTCTGCACTACTGTAAAACTGC CACTCCAAATGCCGATGCATCATAGTATCATATATTGTTGTAAAGTGTCAGAGAGCATAA TCAAGATTAGCTCAAAACCCTCAATAATTTACTCCTATAACTGCATTAAGCTATAAGTGT AATAACTAAAGTTATGCTTTACAAAGCATGATGCAAAGAAATACATTAAATGTCCGATGT ATTAAAAGAATCTATAGAGAGGCAGAAGTTCCTCCCCACATTCTGTATCAAACACAAGTA GTTACTGCTGATTACTCAGAAAGTGAAGCATGCATGTTCTGAAACAAAGATAGTATTTTC TCATTAAACTTCAAGAAATGGATTTTTTTTTTCCCAGCACTGTACCTCAGAGAGATTTTG GCCAGAGACTTATTTCTCCTTTGACCCTGCAGCTCACAGTACCAGCCTGTGCCATACTAG CGCAACTCCAGCATTCAGTACCCTGCCTTTGTCTTTCTCCTGTGGGCATGAACAGCAAAT ACCACAGCAGATTTACCTCTGGAGGCATTTCATAAGCCTCATTCTCAGGATCCACAGGAA TATCAGTATTATTCACCATTCCTTCCTGCAGAAAACCTTCTTCATTCTACATTTAAAACA GGGAGAGAAAAAAATAAGGTGTTAGATCAACTGCTTTTCCAATTTATTGCAAAGCATGTC TTTCCTCTCCACACAGCAGATACTGGCTGTAAAGGCATGCAGAAGTAAGAGAAGGACAAA AGGAATTGGATAGTATCAAGACACGAAAATGAAACATAATTCTATTATGTATTTTGTTAT AGGCAGATAACTCACCCTCCTACACCTTTATTTCATTTTACGGTTTTTACCCTTCTCATA TTACATTTCAAAGTGGCCAAAGGAGGAAGAACAACTATAATTTATTGCATGTTGTTGTTC CCCCCCCCCCCCCCTACAATTTTAGAGCCTAATGACATTGGGAAACGTTTTTCCCTTAAT GAGCCATATTTTTATATCCTTTATTGTGCTGAGTAGCACCTTACTCTGTGCAGTATATTT ATGACACATGACACTGCCTGAStep #1: Using the tools available in this quiz section, identify the exon(s) in the sequence.
Step #2: Identify the organism and gene to which this sequence belongs.
Step #3: Identify the protein sequence of the human gene.
Homework, Due Monday
[homeworkkey]
You work for an institution that studies Parkinson disease. Your lab is starting a new research project involving the study of Niemann Pick Type C. Several labs in the institution are proposing methods to study this protein and its pathway. Your lab specializes in research using the model organism C. elegans. After combing through the literature, your boss concludes that C. elegans would be a great model organism for the study of Parkinson disease. In preparing a research proposal, he asks you to find some basic gene information. Given the protein sequence of the human Niemann Pick Type C protein (NPC1):
1 mtarglalgl lllllcpaqv fsqscvwyge cgiaygdkry nceysgppkp lpkdgydlvq
61 elcpgfffgn vslccdvrql qtlkdnlqlp lqflsrcpsc fynllnlfce ltcsprqsqf
121 lnvtatedyv dpvtnqtktn vkelqyyvgq sfanamynac rdveapssnd kalgllcgkd
181 adacnatnwi eymfnkdngq apftitpvfs dfpvhgmepm nnatkgcdes vdevtapcsc
241 qdcsivcgpk pqpppppapw tilgldamyv imwitymafl lvffgaffav wcyrkryfvs
301 eytpidsnia fsvnasdkge asccdpvsaa fegclrrlft rwgsfcvrnp gcviffslvf
361 itacssglvf vrvttnpvdl wsapssqarl ekeyfdqhfg pffrteqlii rapltdkhiy
421 qpypsgadvp fgppldiqil hqvldlqiai enitasydne tvtlqdicla plspyntnct
481 ilsvlnyfqn shsvldhkkg ddffvyadyh thflycvrap aslndtsllh dpclgtfggp
541 vfpwlvlggy ddqnynnata lvitfpvnny yndteklqra qawekefinf vknyknpnlt
601 isftaersie delnresdsd vftvvisyai mflyislalg hikscrrllv dskvslgiag
661 ilivlssvac slgvfsyigl pltlivievi pflvlavgvd nifilvqayq rderlqgetl
721 dqqlgrvlge vapsmflssf setvafflga lsvmpavhtf slfaglavfi dfllqitcfv
781 sllgldikrq eknrldifcc vrgaedgtsv qasesclfrf fknsysplll kdwmrpivia
841 ifvgvlsfsi avlnkvdigl dqslsmpdds ymvdyfksis qylhagppvy fvleeghdyt
901 sskgqnmvcg gmgcnndslv qqifnaaqld nytrigfaps swiddyfdwv kpqssccrvd
961 nitdqfcnas vvdpacvrcr pltpegkqrp qggdfmrflp mflsdnpnpk cgkgghaays
1021 savnillghg trvgatyfmt yhtvlqtsad fidalkkarl iasnvtetmg ingsayrvfp
1081 ysvfyvfyeq yltiiddtif nlgvslgaif lvtmvllgce lwsavimcat iamvlvnmfg
1141 vmwlwgisln avslvnlvms cgisvefcsh itraftvsmk gsrveraeea lahmgssvfs
1201 gitltkfggi vvlafaksqi fqifyfrmyl amvllgathg liflpvllsy igpsvnkaks
1261 cateerykgt ererllnf
Question #1: Find the closest homolog to NPC1 in C. elegans.
Question #2: On what C. elegans chromosome does the homolog reside?
Question #3: Find and give the accession number of at least one EST containing the C. elegans homolog
Question #4 What can we find out from searching ESTs? What information is gained from this information?
Question #5: Bonus Question Using the C. elegans genome browser see if you can figure out where the C. elegans orthologue is expressed in worms
Mail your answers to maxboeck@u.washington.edu